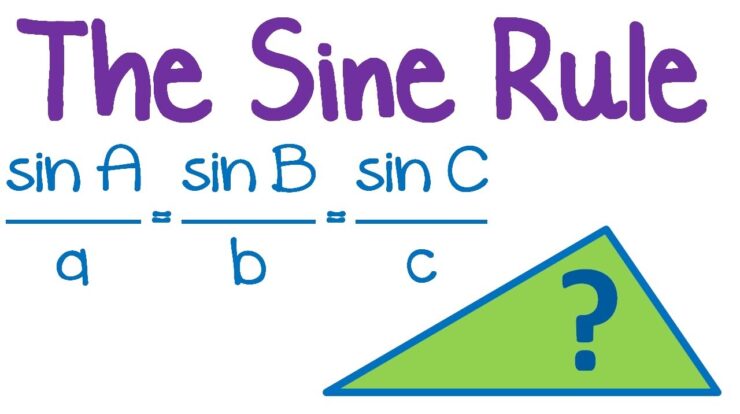
Introducing sine meaning, a concept that forms the cornerstone of trigonometry and finds widespread applications in diverse fields. From its etymological origins to its mathematical definition, properties, and graphical representation, this article delves into the fascinating world of sine.
As a trigonometric function, sine is defined as the ratio of the length of the side opposite an angle in a right triangle to the length of the hypotenuse. It plays a crucial role in modeling periodic phenomena, such as sound waves and oscillations, and has significant applications in engineering, physics, and music.
Sine Function
The sine function, denoted as sin(x), is a fundamental trigonometric function that plays a vital role in various fields of mathematics, science, and engineering.
Etymology of Sine
The term “sine” originates from the Latin word “sinus,” meaning “bay” or “curve.” It was first used in astronomy to describe the vertical coordinate of a point on a circle, particularly in the context of the daily motion of the Sun.
Mathematical Definition of Sine
In mathematics, sine is defined as the ratio of the length of the side opposite an angle in a right-angled triangle to the length of the hypotenuse.
Properties of Sine
Sine possesses several key properties:
- Periodicity: Sine repeats its values over a period of 2π.
- Amplitude: The maximum value of sine is 1, while the minimum value is -1.
- Symmetry: Sine is an odd function, meaning it is symmetrical about the origin.
Applications of Sine
Sine finds applications in a wide range of fields, including:
- Physics: Describing oscillatory motion, such as the motion of a pendulum.
- Engineering: Calculating forces and stresses in structures.
- Music: Analyzing sound waves and musical intervals.
Inverse Sine Function, Sine meaning
The inverse sine function, denoted as arcsin(x), is the inverse of the sine function.
Graphical Representation of Sine
The graph of the sine function is a sinusoidal curve that oscillates between -1 and 1.
Related Trigonometric Functions
Sine is closely related to other trigonometric functions, such as cosine and tangent:
- Cosine: Cosine is defined as the ratio of the length of the side adjacent to an angle in a right-angled triangle to the length of the hypotenuse.
- Tangent: Tangent is defined as the ratio of the length of the opposite side to the length of the adjacent side in a right-angled triangle.
Last Recap
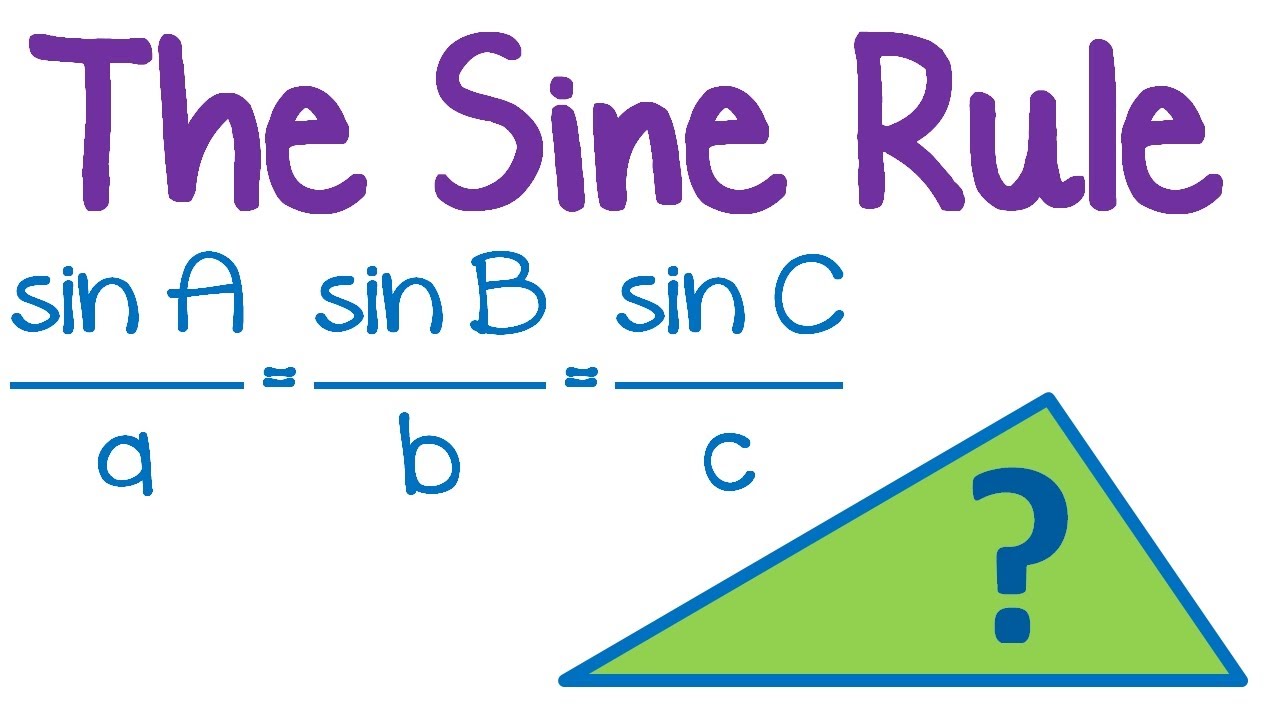
In conclusion, sine meaning encompasses a rich tapestry of mathematical concepts and practical applications. Its versatility and ubiquity make it an indispensable tool for understanding and solving problems across various disciplines. Whether it’s calculating the height of a building or analyzing the vibrations of a musical instrument, sine continues to captivate and inspire.
Helpful Answers: Sine Meaning
What is the etymology of the term “sine”?
The term “sine” originates from the Latin word “sinus,” meaning “bay” or “curve,” which was used to describe the shape of the function’s graph.
How is sine used in physics?
Sine is used in physics to model oscillatory motion, such as the motion of a pendulum or the vibration of a spring. It helps determine the displacement, velocity, and acceleration of objects undergoing periodic motion.